Does Drinking Alcohol Raise Cholesterol?
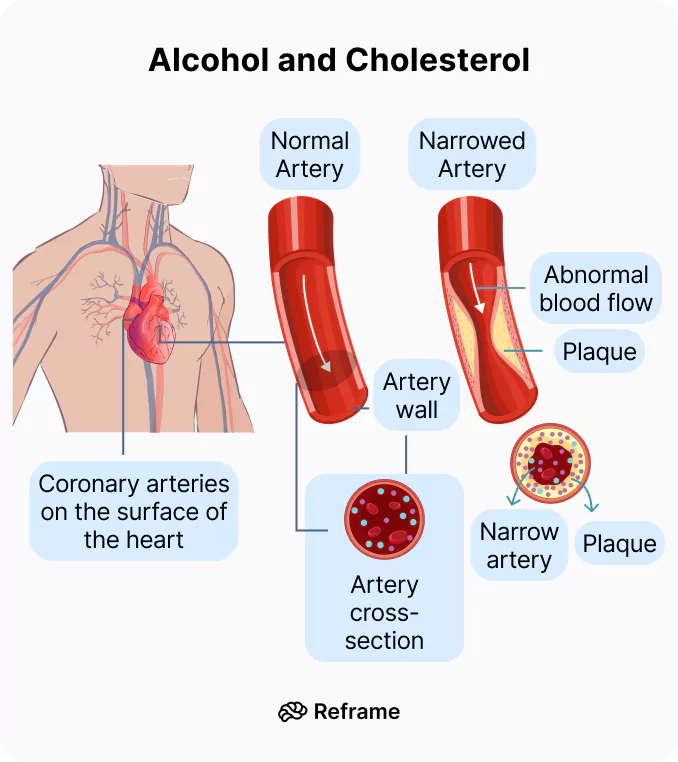
Excessive alcohol consumption can significantly impact cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health. Alcohol, particularly beer, sugary cocktails, and spirits mixed with high-calorie beverages, contributes to increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL), commonly known as “bad” cholesterol, while also reducing high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the “good” cholesterol responsible for removing excess cholesterol from the bloodstream. Additionally, alcohol raises triglyceride levels, a type of fat in the blood that, when elevated, increases the risk of heart disease and pancreatitis. Regular heavy drinking can also lead to fatty liver disease, impairing the liver’s ability to regulate cholesterol and fat metabolism effectively. Furthermore, excessive alcohol intake contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance, both of which are closely linked to high cholesterol and an increased risk of cardiovascular conditions such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart attacks, and strokes. Therefore, limiting alcohol consumption and maintaining a balanced lifestyle are essential for managing cholesterol levels and promoting long-term heart health.

Drinking alcohol has a more significant effect on cholesterol than most people think. Alcohol has a unique way of destroying human organs when overconsumed and frequently used. Alcohol is effectively causing your low-density lipoprotein (LDL, bad cholesterol) to rise when you drink too much of it. Other factors play a significant role when a person is highly intoxicated with alcoholic beverages. Typically, a drunk person can be so dehydrated that when their blood mixes with the alcohol, it can become so thick and create clots and blockages. Once in a blue moon, use of alcohol is not as bad as everyday users. I suggest avoiding alcohol at all costs if you’re told by a doctor that you have bad cholesterol. Many people don’t know if they have high cholesterol because, like any other cardiovascular system damage, it is often asymptomatic. The best way to keep check of your internal organs and overall health is by consulting with your primary doctor. If you don’t have medical insurance, check with your local clinic about how to obtain one. The third option is to pay out of your pocket. Doctors will determine if you have high cholesterol by performing blood work on you, which they withdraw blood into a tube for testing. The test result usually comes in within a week or two. You must do this blood work regularly, at least once a year or twice a year, for adults over the age of 60. A person with high cholesterol can follow the lifestyle guidelines I put together on this site. 1. Regular exercise can help get alcohol out of your system faster. As a way to get your blood stream from clotting to flowing formally. Also, keep yourself hydrated at all times. 2. Healthy Nutrition is by far the most effective way to get your cholesterol to a normal degree. Choosing the right food for your HDL and LDL will benefit your cardiovascular system; just once alcohol use a week wouldn’t hurt that bad. 3. Smoking cigarettes has a similar effect on high cholesterol, and it’s as necessary to avoid smoking at all cost because it has a high likelihood of causing arteries damage. A person who mixes alcohol and smoking all together has a higher risk of bad cholesterol or even more severe heart health complications.
Here is a list of what drinking alcohol causes high cholesterol.
1. Increased LDL (Bad Cholesterol)
- Alcohol, especially beer, cocktails, and sugary drinks, can raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the “bad” cholesterol that contributes to plaque buildup in arteries.
2. Decreased HDL (Good Cholesterol)
- While moderate alcohol consumption may increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL), excessive drinking can lower HDL levels, reducing its protective effect against heart disease.
3. Fatty Liver Disease
- Alcohol increases fat accumulation in the liver, leading to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD), which can worsen cholesterol metabolism.
4. High Triglyceride Levels
- Alcohol is high in sugars and calories, increasing triglyceride levels, which contributes to heart disease, pancreatitis, and metabolic syndrome.
5. Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
- Excessive alcohol consumption raises blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and atherosclerosis (artery hardening due to cholesterol buildup).
6. Obesity and Weight Gain
- Alcohol is high in empty calories and can lead to weight gain, which is a major risk factor for high cholesterol and heart disease.
7. Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke
- High cholesterol from excessive drinking can cause arterial plaque buildup, leading to atherosclerosis, heart attacks, and strokes.
8. Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
- Alcohol can interfere with blood sugar control, leading to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, which are linked to high cholesterol and heart complications.
Conclusion:
While moderate drinking (e.g., a glass of wine occasionally) may have some benefits, excessive alcohol consumption significantly worsens cholesterol levels and increases the risk of heart disease, liver damage, and metabolic disorders. Reducing alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage cholesterol levels and protect overall health.